
Intrinsic muscles of the foot. Plantar intrinsics Layer 1 1 =... Download Scientific Diagram
It is a dorsiflexor of the ankle. Origin: Upper 1/2 of lateral and anterior surfaces of the tibia. Insertion: Inner surface of the medial cuneiform and 1st metatarsal. Actions: Inversion & Dorsiflexion. Innervation: Deep peroneal nerve. Daily uses: Walking - to lift the foot up and clear the ground.
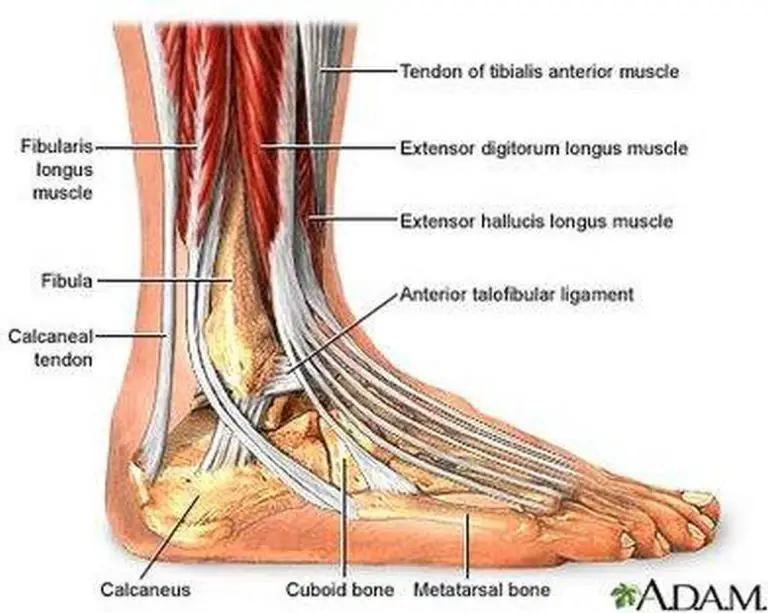
Pictures Of Ankle Muscles
Basic Foot and Ankle Anatomy - Muscles and Fascia Description Muscle s are responsible for movement and the primary cause of ankle and foot injuries is when a movement is performed excessively, repetitively, and for a long duration that exceeds tissue capabilities. [1]

Foot and Ankle Musculoskeletal Key
LABELED DIAGRAMS. Figure 1. Sections and Bones of the Foot A. Lateral (Left) B. Anterior (Right) Figure 2. Compartments of the Foot A. Cut Section through Mid-Foot. Figure 3. First Layer of the Foot A. Plantar View of Right Foot. Figure 4. Second Layer of the Foot A. Plantar View of Right Foot.

Pin on Body (of) Work
The foot is an intricate part of the body, consisting of 26 bones, 33 joints, 107 ligaments, and 19 muscles. Scientists group the bones of the foot into the phalanges, tarsal bones, and.
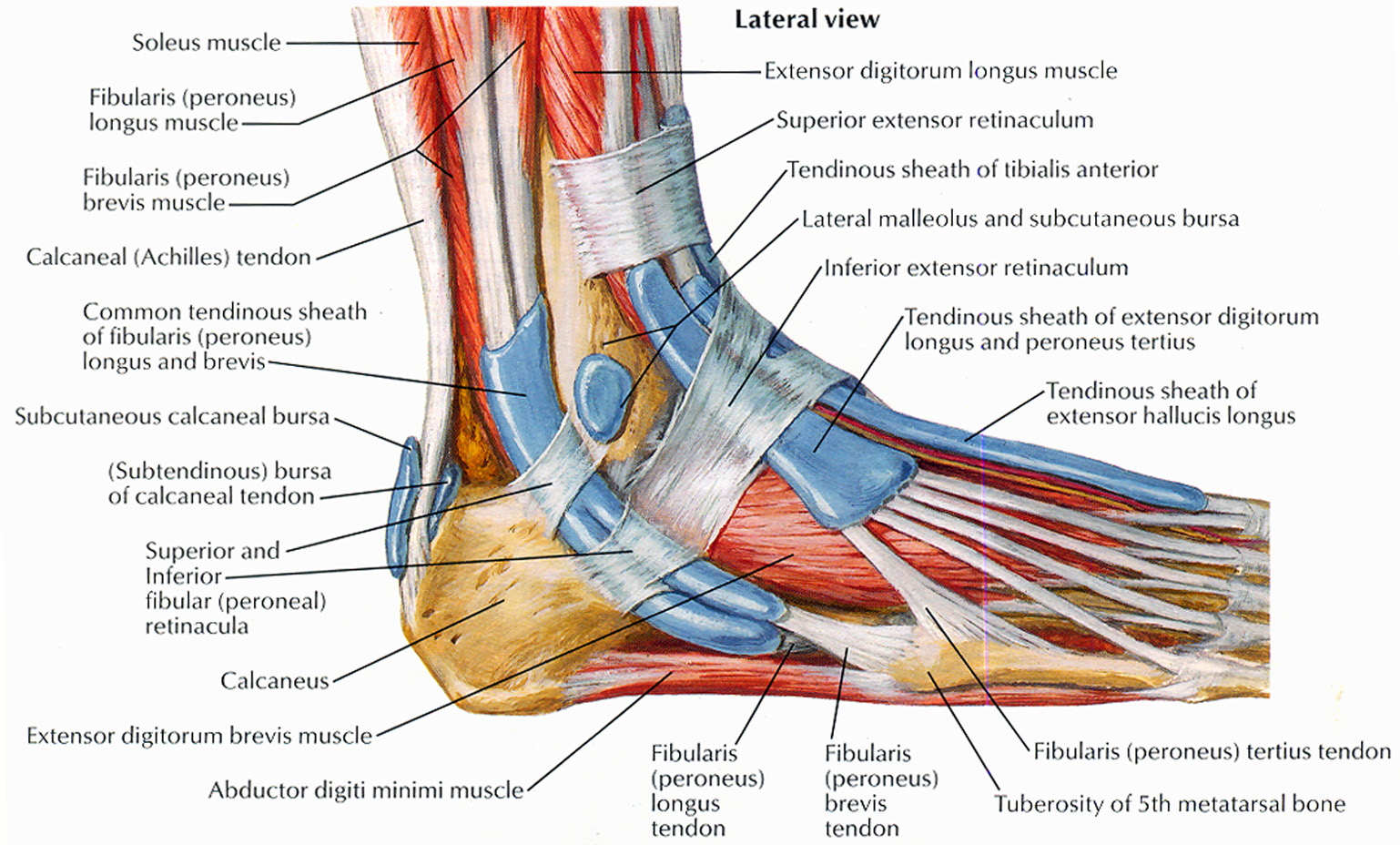
Muscles that lift the Arches of the Feet
The muscles of the foot are located mainly in the sole of the foot and divided into a central (medial) group and a group on either side (lateral). The muscles at the top of the foot fan out to supply the individual toes. The tendons in the foot are thick bands that connect muscles to bones.

Human Anatomy for the Artist The Dorsal Foot How Do I Love Thee? Let Me Count Your Tendons
Anatomy Explorer Abductor Digiti Minimi Muscle of Foot Abductor Hallucis Muscle Adductor Brevis Muscle Adductor Longus Muscle Adductor Magnus Muscle Biceps Femoris Muscle (Long Head) Biceps Femoris Muscle (Short Head) Calcaneal (Achilles) Tendon Dorsal Interosseous Muscles of Foot Extensor Digitorum Longus Muscle Extensor Hallucis Brevis Muscle
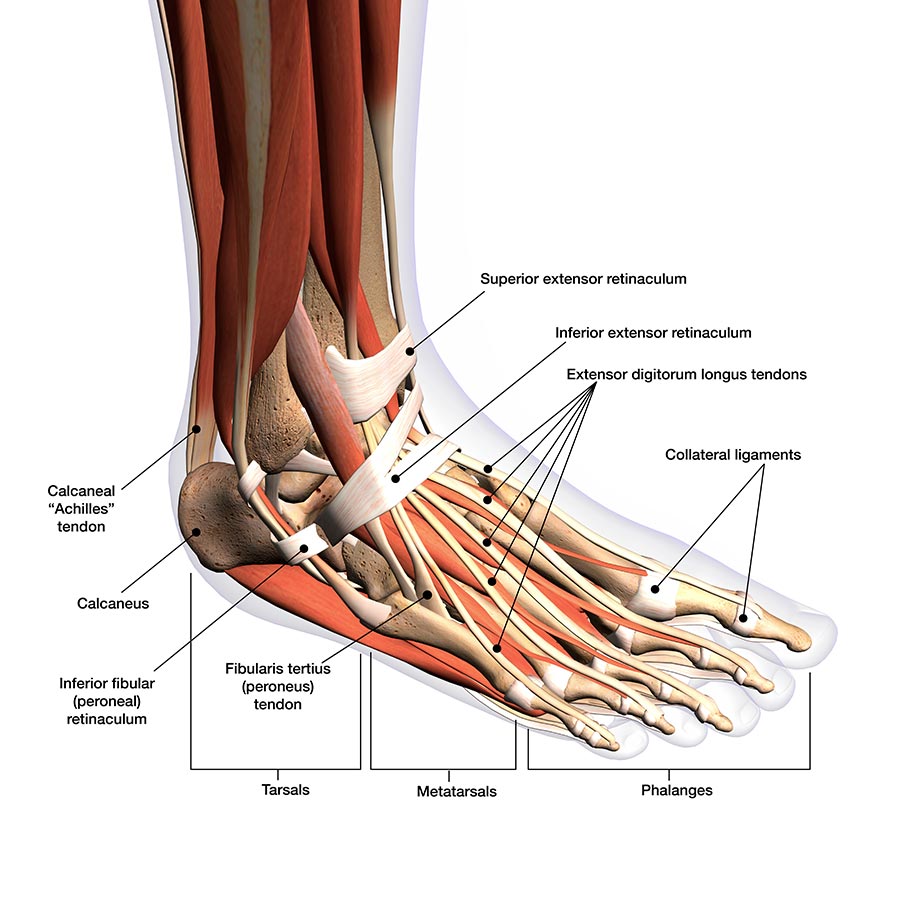
Foot and ankle anatomy, conditions and treatments
Ankle anatomy The ankle joint, also known as the talocrural joint, allows dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot. It is made up of three joints: upper ankle joint (tibiotarsal), talocalcaneonavicular, and subtalar joints. The last two together are called the lower ankle joint.
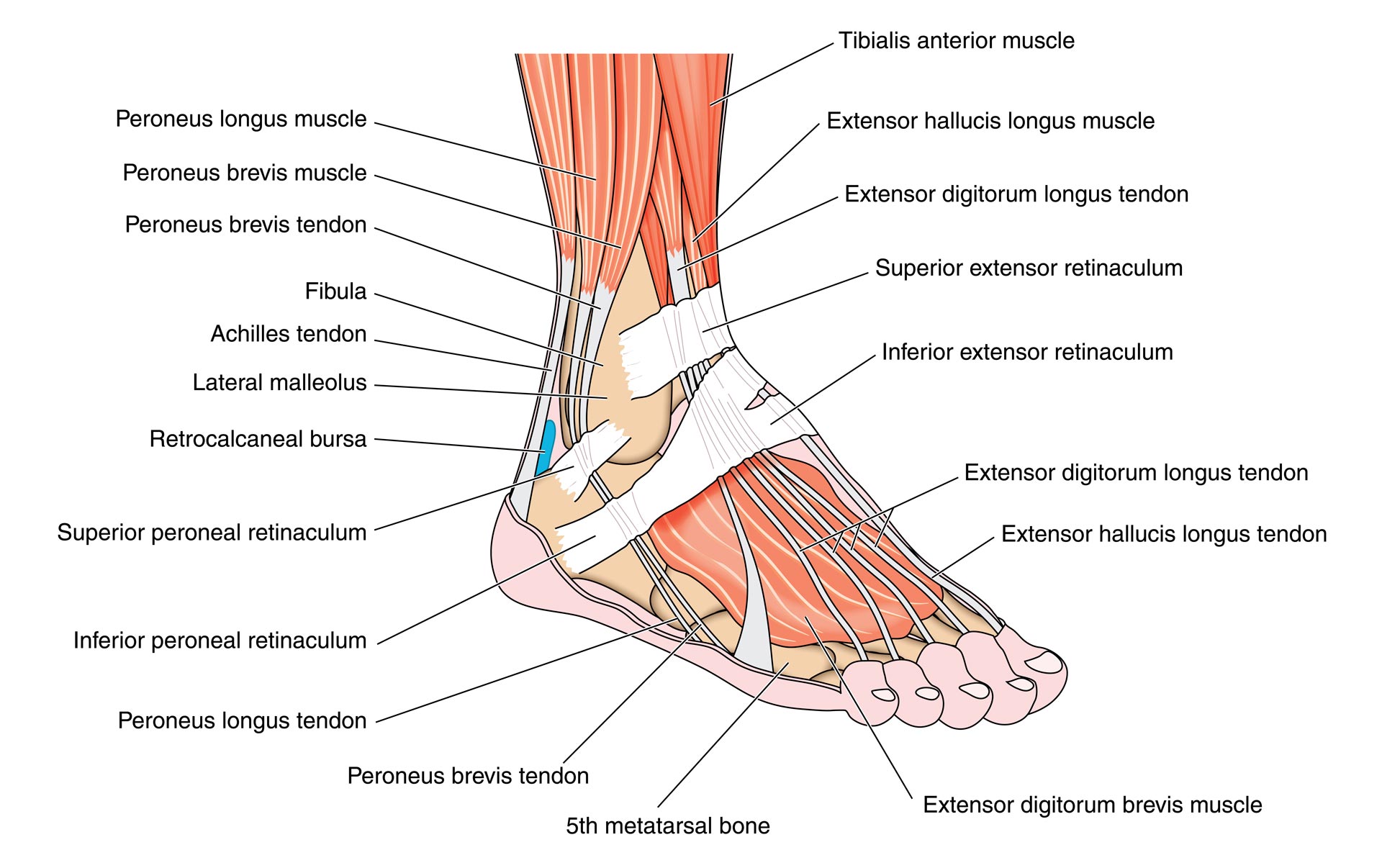
Common Ankle & Foot Disorders Comprehensive Diagnosis & Treatment
Nearly one-fourth of the body's bones are in our feet. The bones of the feet are: Talus - the bone on top of the foot that forms a joint with the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and fibula.; Calcaneus - the largest bone of the foot, which lies beneath the talus to form the heel bone.; Tarsals - five irregularly shaped bones of the midfoot that form the foot's arch.
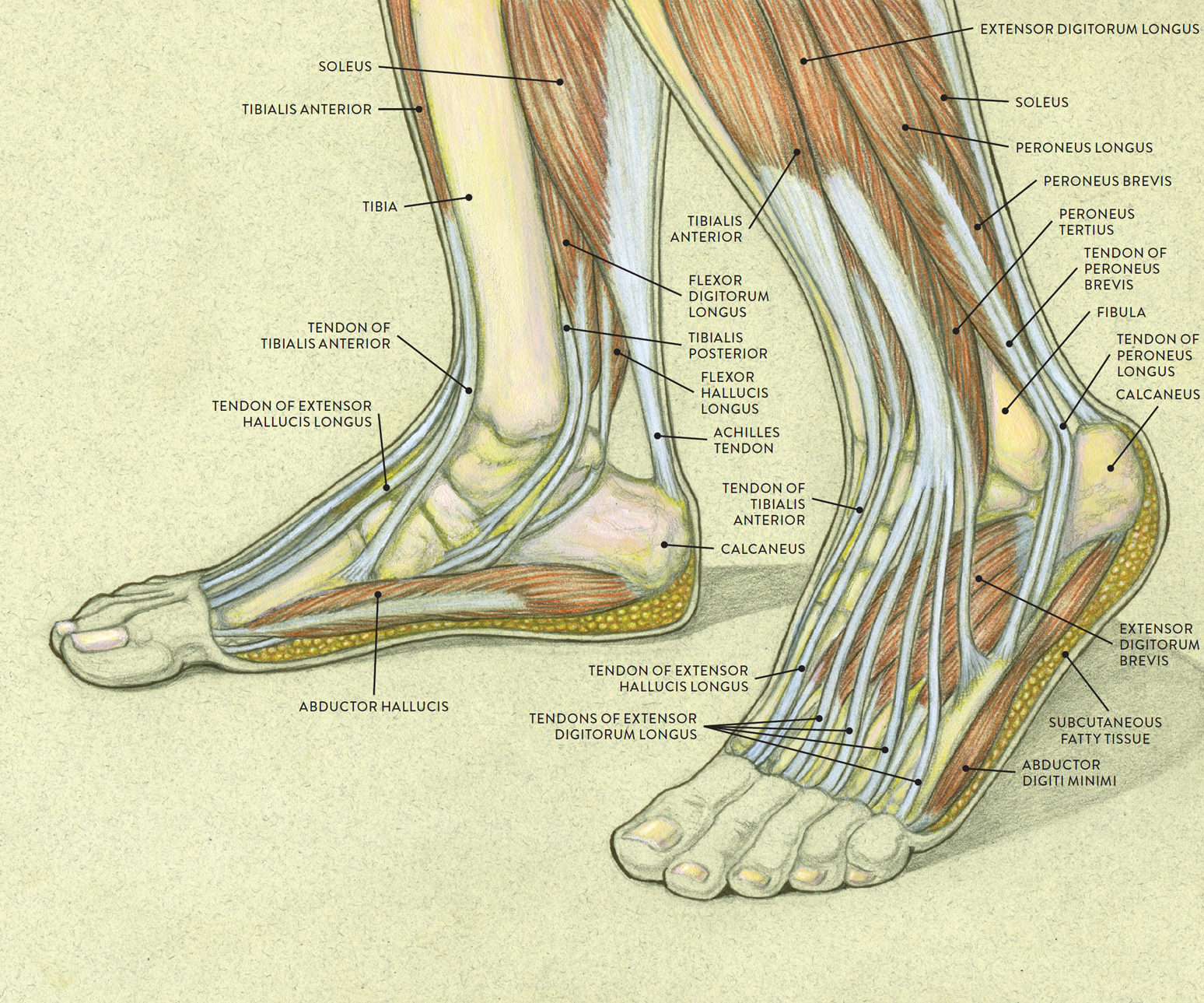
Tendon Diagram Leg / Cardiovascular System of the Leg and Foot nadilughaharabiahwall
Anatomy and functions of the dorsal muscles of the foot shown with 3D model animation. The muscles of the dorsum of the foot are a group of two muscles, which together represent the dorsal foot musculature. They are named extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis . The muscles lie within a flat fascia on the dorsum of the foot.

Muscle Anatomy Of The Plantar Foot Everything You Need To Know Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Muscle
There are 29 muscles associated with the human foot: 10 originate outside the foot but cross the ankle joint to act on the foot, and 19 are intrinsic foot muscles. The foot is crucial to human locomotion and postural stability, and the muscles associated with the foot are therefore involved principally in this function.
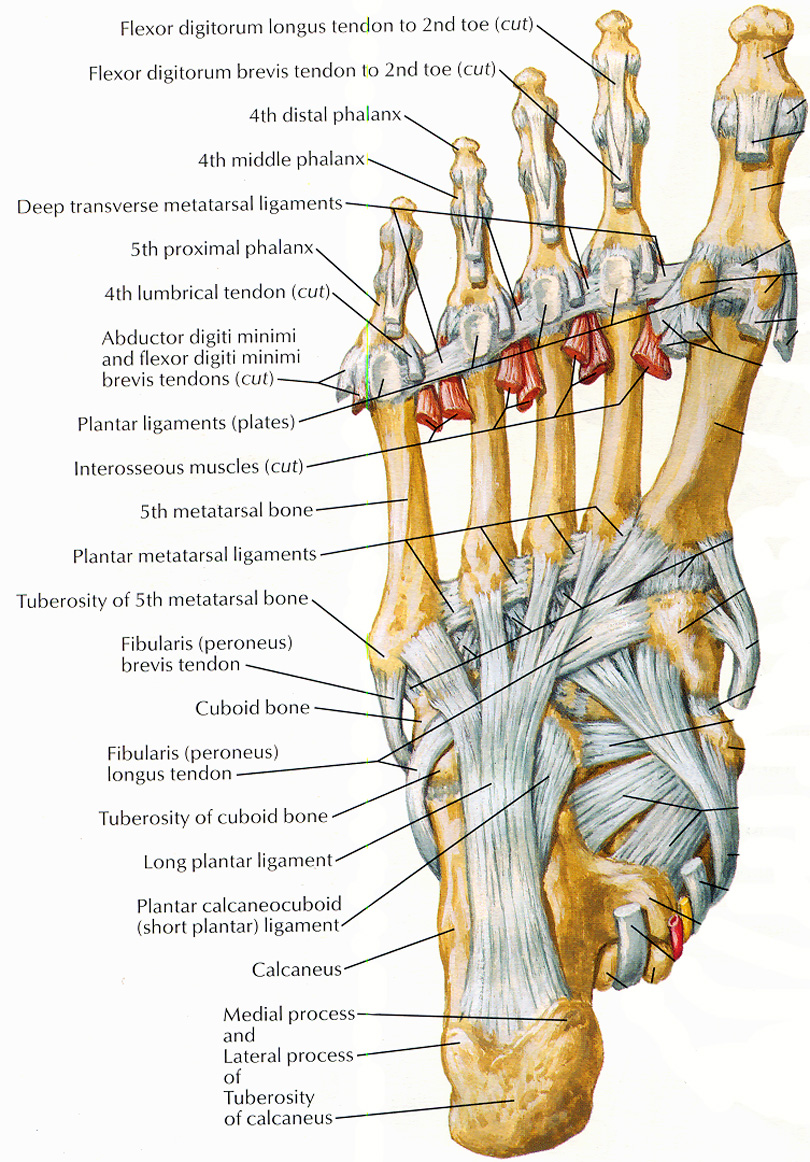
Muscles that lift the Arches of the Feet
Introduction The foot is anatomically defined as the distal part of the lower extremity and encompasses all structures below the ankle joint. The muscles of the foot can be split into two groups, the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. The extrinsic foot muscles are found in the lower leg and act to dorsiflex, plantarflex, invert and evert the foot.

Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs · Anatomy and Physiology
The Anatomy of Feet: Bones and Structure The foot is composed of 26 bones, making up about one-quarter of all the bones in the human body. These bones are divided into three main regions: the hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot.

Loading... Human anatomy chart, Foot anatomy, Nerve anatomy
1. Foot Bones When thinking about foot and ankle anatomy, we usually divide the into three categories: the hindfoot, midfoot and forefoot. the hindfoot comprises of the ankle joint, found at the bottom of the leg. This is where the ends of the shin bones, the . Underneath this is the heel bone, aka the
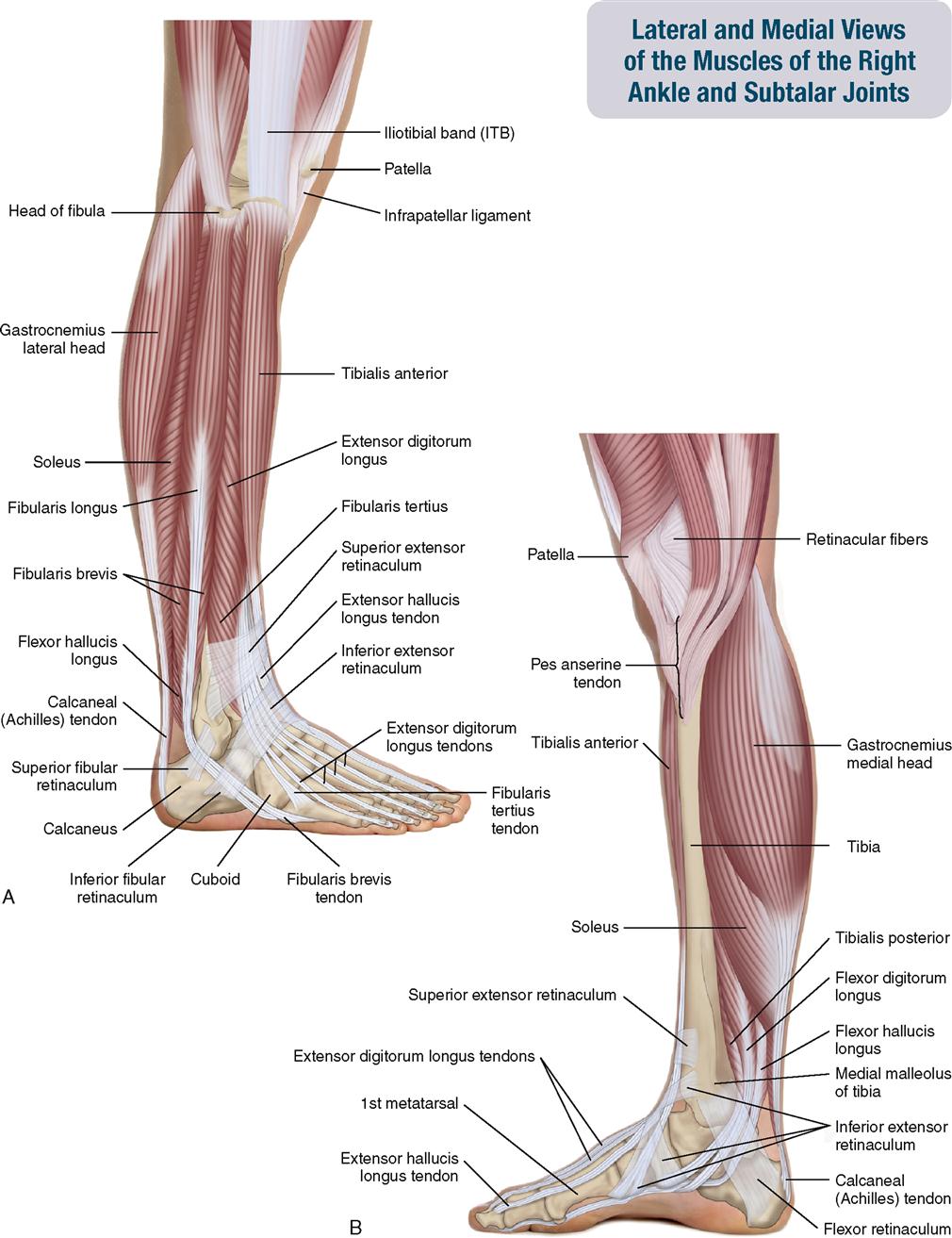
11. Muscles of the Leg and Foot Musculoskeletal Key
The foot is a complex part of the body that is made up of many bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. It can easily be injured, develop diseases, or get infections. Bunions, claw toes, flat feet, hammertoes, heel spurs, mallet toes, metatarsalgia, Morton's neuroma, and plantar fasciitis are a few examples of foot problems that commonly cause pain.

The extrinsic muscles that move the foot. Human muscle anatomy, Human body anatomy, Muscle anatomy
33 joints more than 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments Bones of the foot The bones in the foot make up nearly 25% of the total bones in the body, and they help the foot withstand weight..

Foot and Ankle Musculoskeletal Key
Tibia Fibula Talus Cuneiforms Cuboid Navicular Many of the muscles that affect larger foot movements are located in the lower leg. However, the foot itself is a web of muscles that can.